Structural analysis just got smarter with the release of STKO version 4. This update delivers innovative tools to simplify workflows and enhance accuracy. The latest features range from improved post-processing animations to advanced material modeling techniques like cohesive zones and bond-slip models. Users can also enjoy automated mass assignment and constraint handling processes, making projects more efficient.
Below, we’ll explore the highlights of STKO 4.0.0 in detail, breaking down what’s new and how to use it.
Updates for Better Workflows and Results
STKO 4.0.0 focuses on making structural engineering easier and more accurate. Whether you’re running complex masonry models or setting up animations, these improvements will save time and offer better insights.
Compatibility with OpenSees 3.7.0
To access the full potential of STKO 4.0.0, you’ll need OpenSees version 3.7.0. This ensures all features are fully functional and optimized for seamless integration.
Categories of New Features
- GUI Upgrades: New visual tools for shell extrusions.
- Post-Processing Enhancements: Custom transformation options and smoother animations.
- Material Model Innovations: Updates for ASDConcrete3D and the introduction of ASDConcrete1D.
- Beta Features: Experimental tools like automated absorbing boundary updates.
Enhanced Visualization and Animation Tools
Shell Extrusions for Better Modeling
You can now add visual representation for shell extrusions, a feature previously limited to beam elements. While it’s purely cosmetic, it helps make models easier to understand and analyze. This is especially useful for geometries using shell-element cross-sections.
Build Symmetrical Models with Ease
Symmetry-based modeling just got a boost. New post-processing transformations let you mirror, scale, rotate, or customize models to reflect entire structures. For example, users working with quarter-cylinder sections can reconstruct the full model for better visualization.
Custom Transformation Highlights
- Apply transformations like mirroring and scaling using clear user inputs.
- No extra memory usage: Transformations apply directly to visualization plots, not data files.
- Fine-tune the creation process with a 3×3 matrix for complete control.
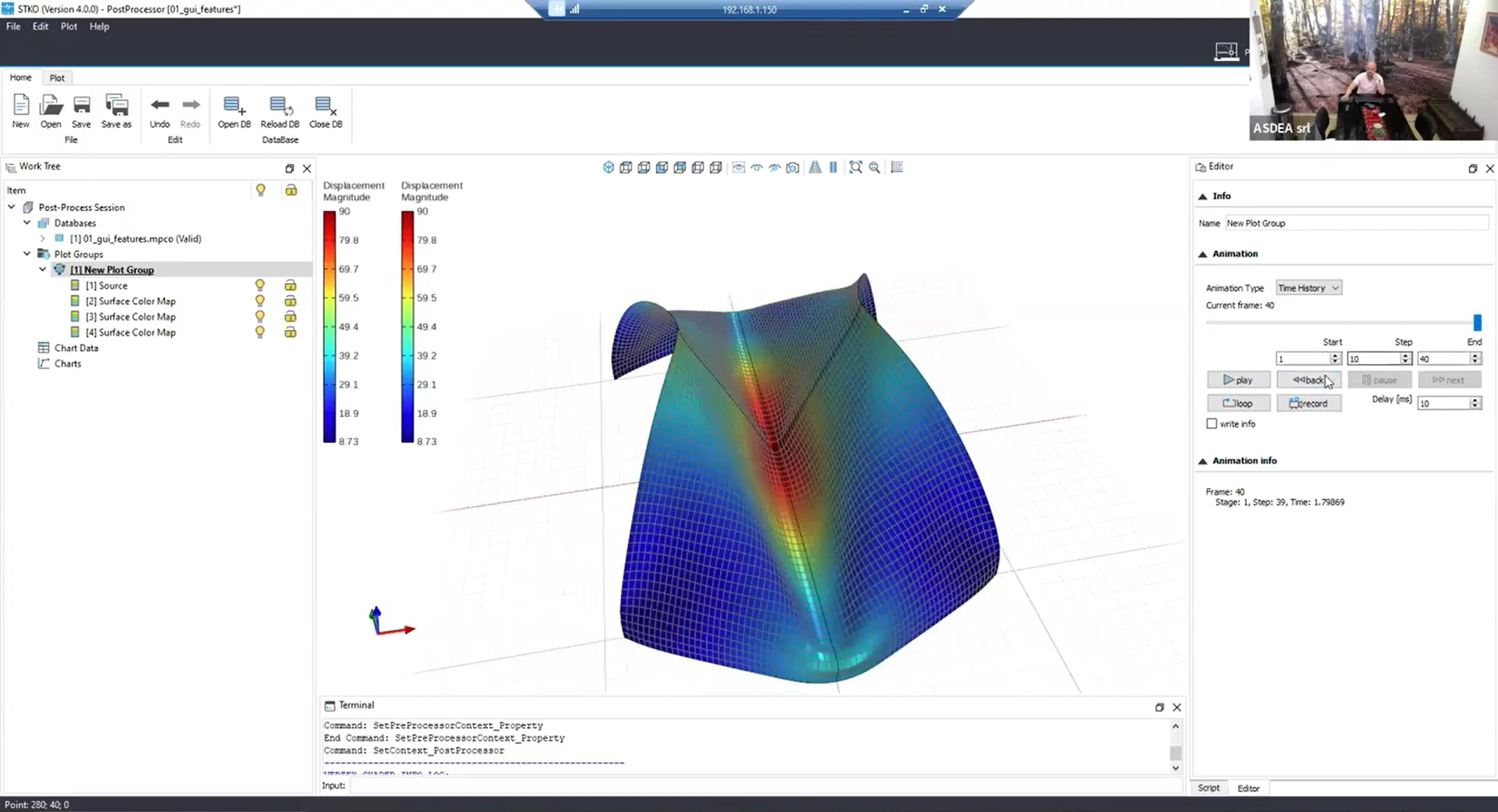
Smarter Animations
Animations now support frame-step functionality. If you’re working with large models, this lets you skip frames to reduce computing time. Parallel rendering creates smoother, better-synced visuals.
Advanced Material Modeling
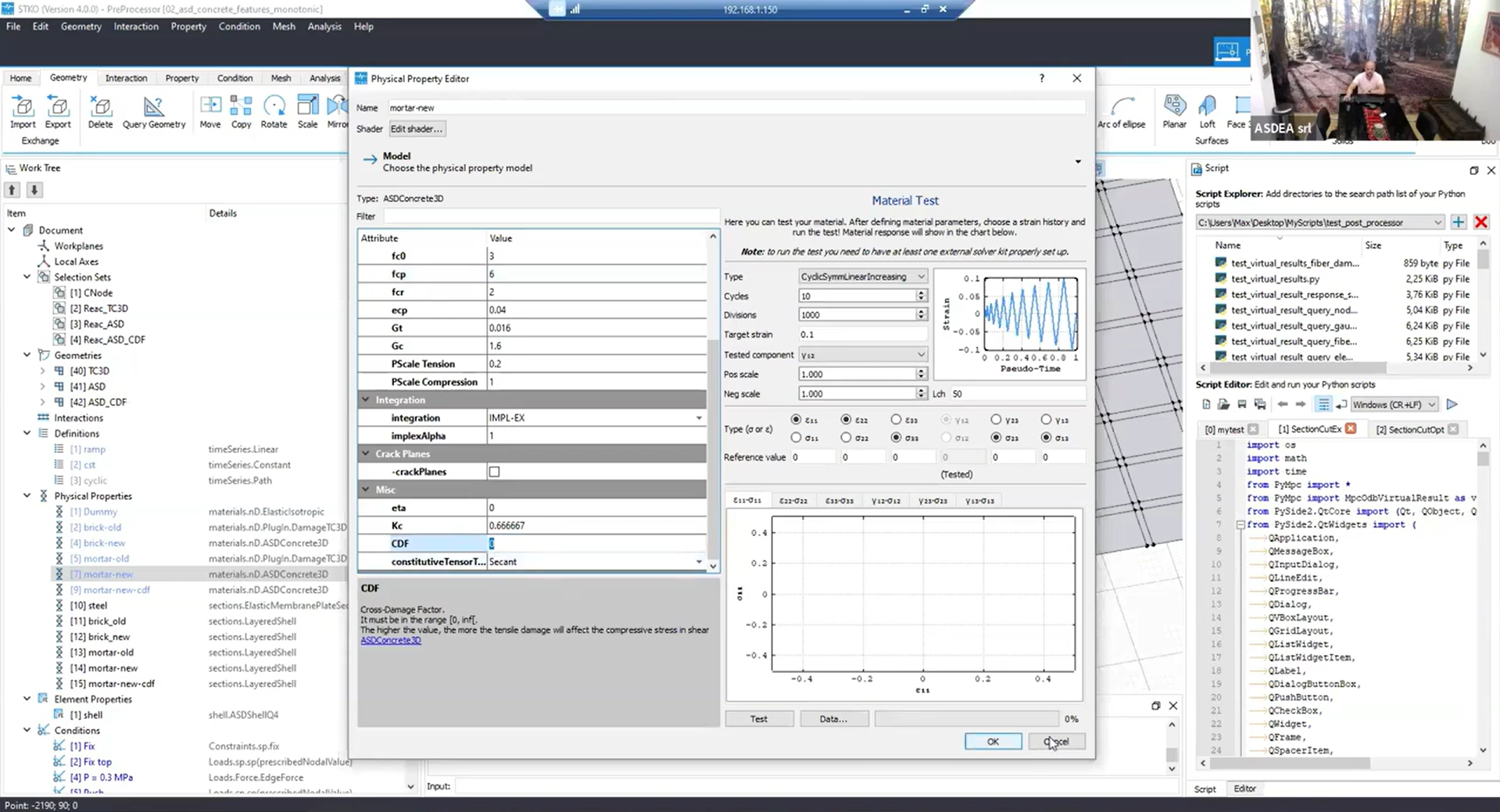
Refinements in ASDConcrete3D
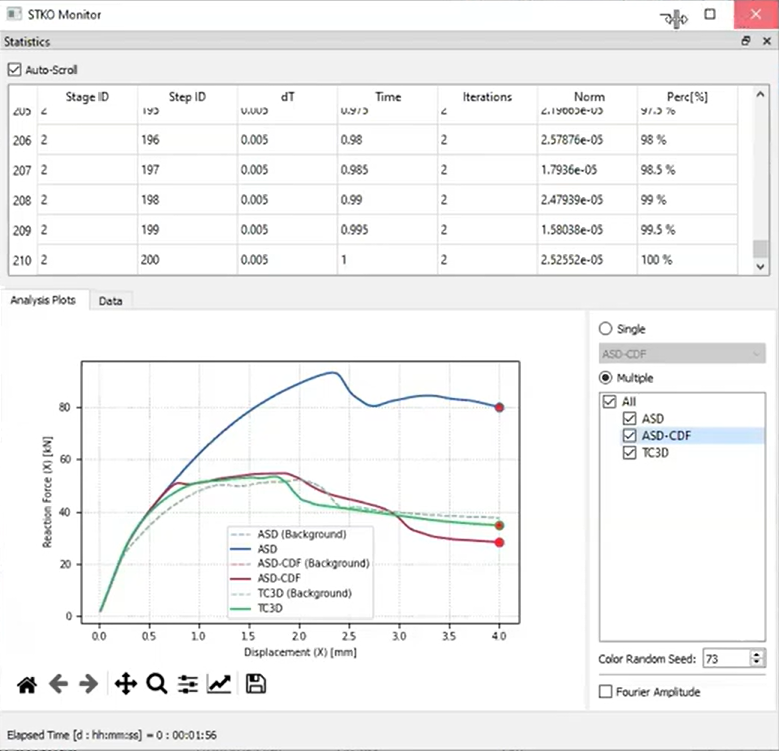
For masonry and other non-concrete materials, the ASDConcrete3D model now offers customizable parameters. The Cross Damage Factor (CDF) helps control dilatancy more effectively, correcting overestimations for materials like mortar.
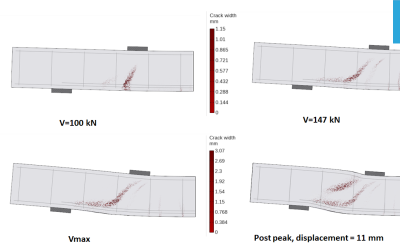
Use Case: Micro-Modeling Masonry Structures
By combining bricks and mortar in micro-models, engineers can simulate complex behaviors such as cracking. Adjusting the CDF parameter avoids overestimating shear strength, delivering more accurate predictions for monotonic and cyclic tests.
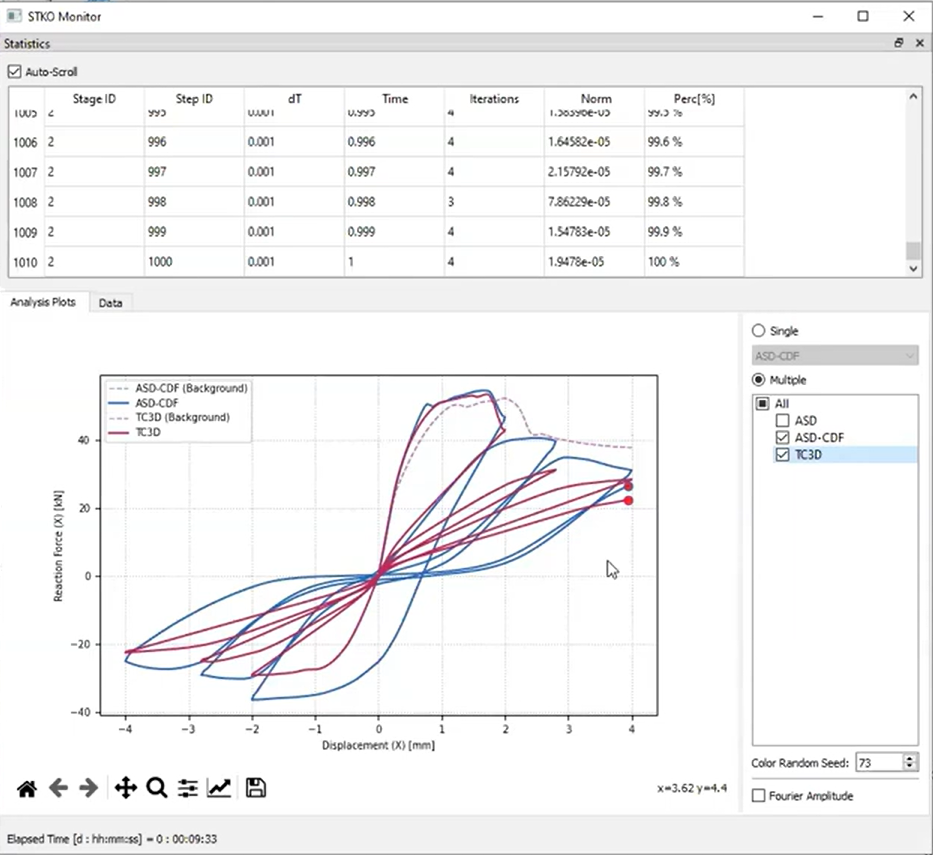
Improved Cyclic Behavior
ASDConcrete3D shows better pinched hysteresis during cyclic testing compared to the older damage TC 3D model. This makes it ideal for simulations requiring realistic cyclic loading responses, such as masonry under repeated load conditions.
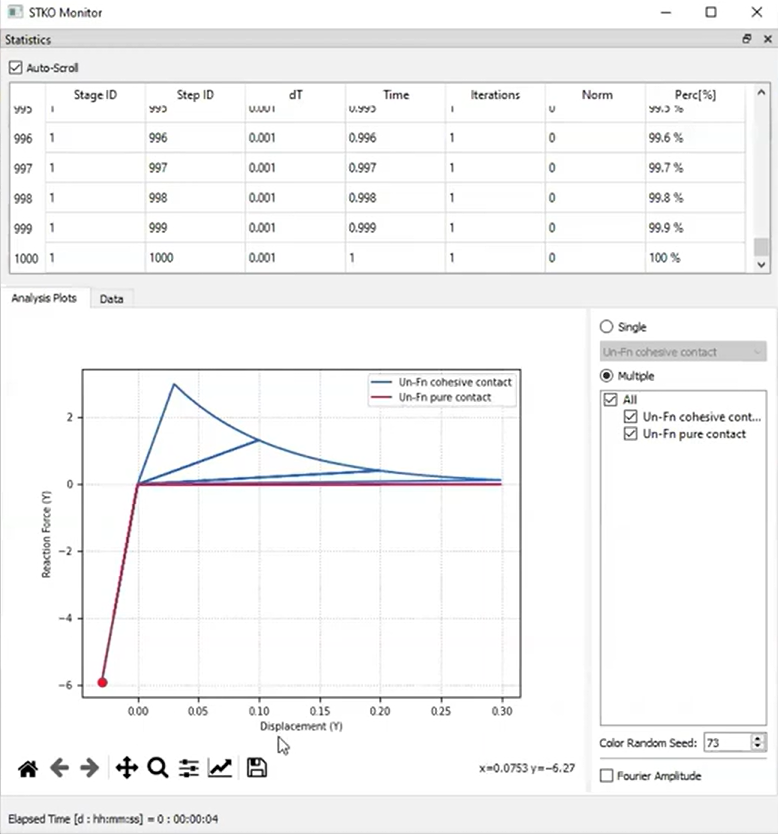
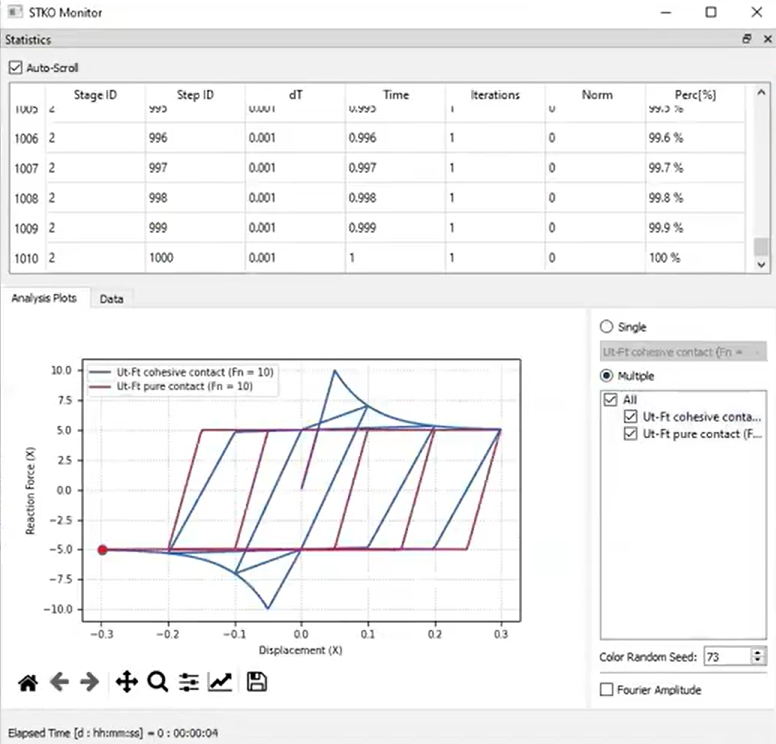
Modeling Cohesive Zones in Contact Elements
Cohesive zones are now available for zero-length contact elements. This allows users to simulate thin adhesive or mortar layers with cohesive properties. It’s particularly useful for masonry and layered material analysis.
Automating the Process
To implement cohesive zones, STKO creates two zero-length elements behind the scenes: one for pure contact and another for cohesive properties. Normal tensile strength, cohesion, and fracture energy can all be defined.
Examples of Cohesive Behavior
- Normal Behavior: Elastic to softening response under tensile loads.
- Tangential Behavior: Shear resistance that progressively degrades with sliding.
Streamlined Mass Assignment
Assigning mass to beam elements in OpenSees used to be tedious. STKO 4.0.0 introduces an automatic edge mass feature. Supply the material density and cross-section data, and the software calculates the mass per unit length or converts it into self-weight loads.
With buildings containing hundreds of cross-sections, this automation cuts down on manual errors and labor.
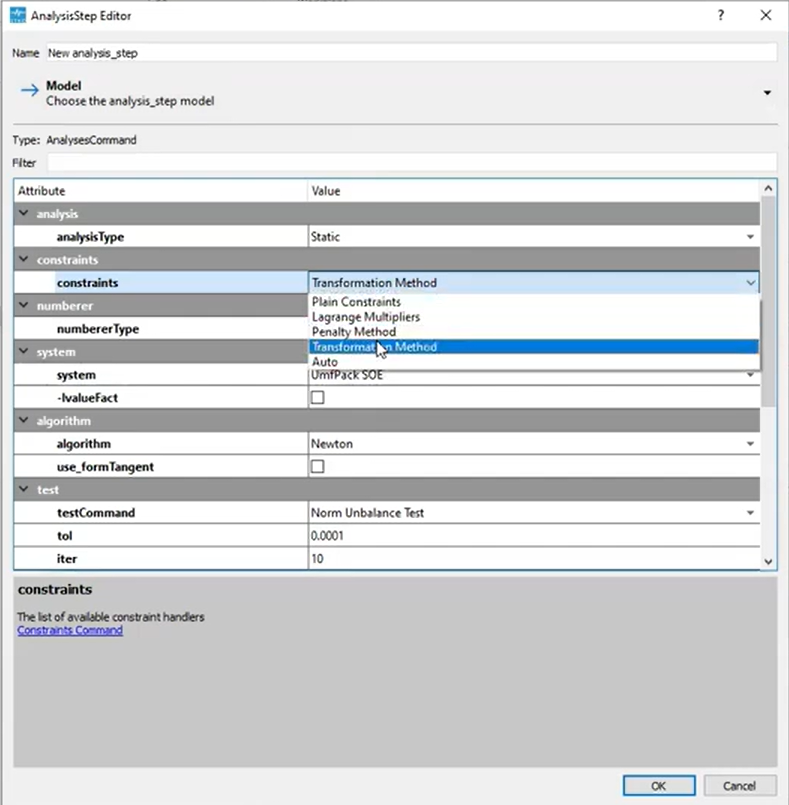
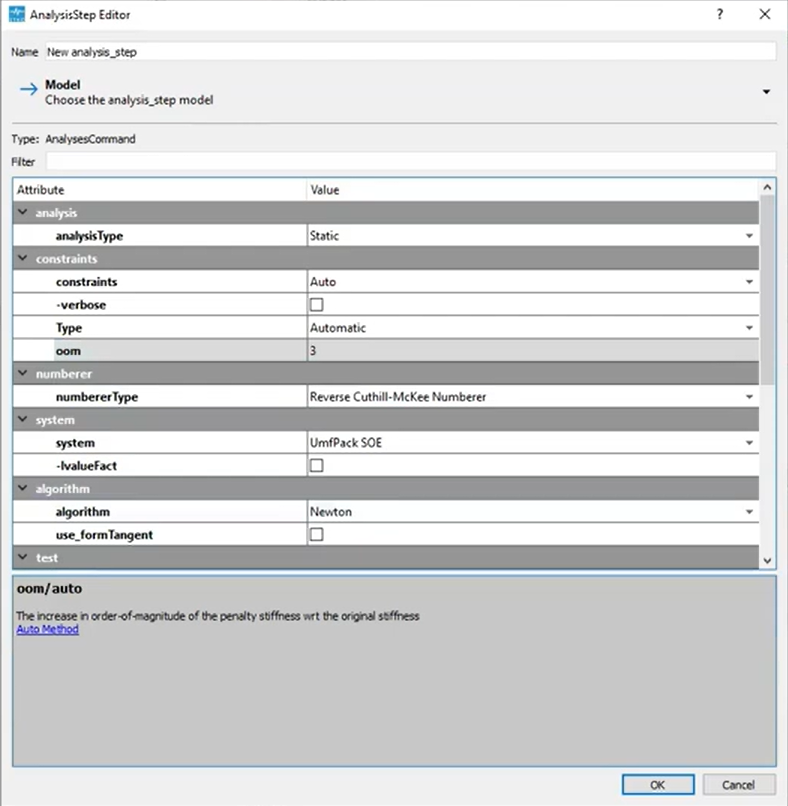
Flexible Constraint Handling
Constraints don’t have to create headaches anymore. The Auto Constraint Handler merges the best of two worlds:
- Single-Point Constraints: Handled via the transformation method for exact enforcement.
- Multi-Point Constraints: Addressed using penalty methods to avoid conflicts.
When unsure about penalty values, enable automatic calculations, and let the program select an optimized value based on local stiffness.
Parallel and Initial Strain Materials
Parallel Material Wrappers
Parallel wrappers let you stack multiple material behaviors. Create complex hybrids by summing their effects, whether for concrete, steel, or composites.
Initial Strain for Static and Time-Dependent Behavior
This wrapper introduces predefined strain conditions to simulate effects like shrinkage or creeping. Apply strains incrementally to avoid convergence issues during nonlinear analyses.
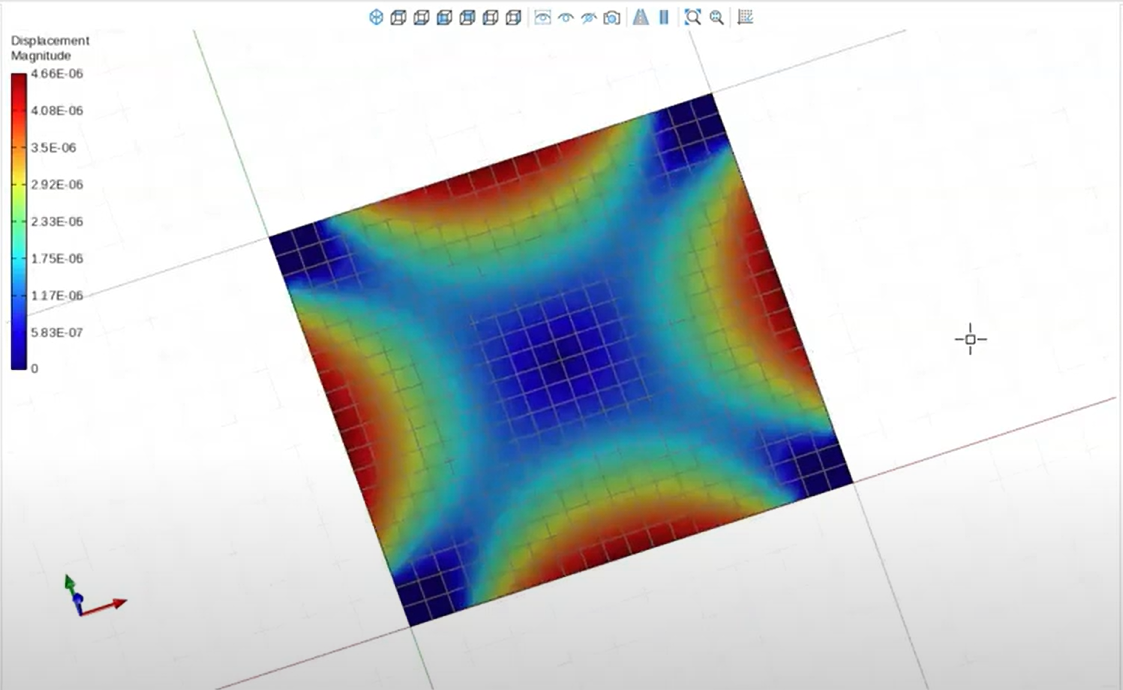
Example: Fracture Propagation
By gradually increasing initial strain, cracks propagate more naturally. This is helpful when modeling slabs under constrained edge conditions or thermal loading scenarios.
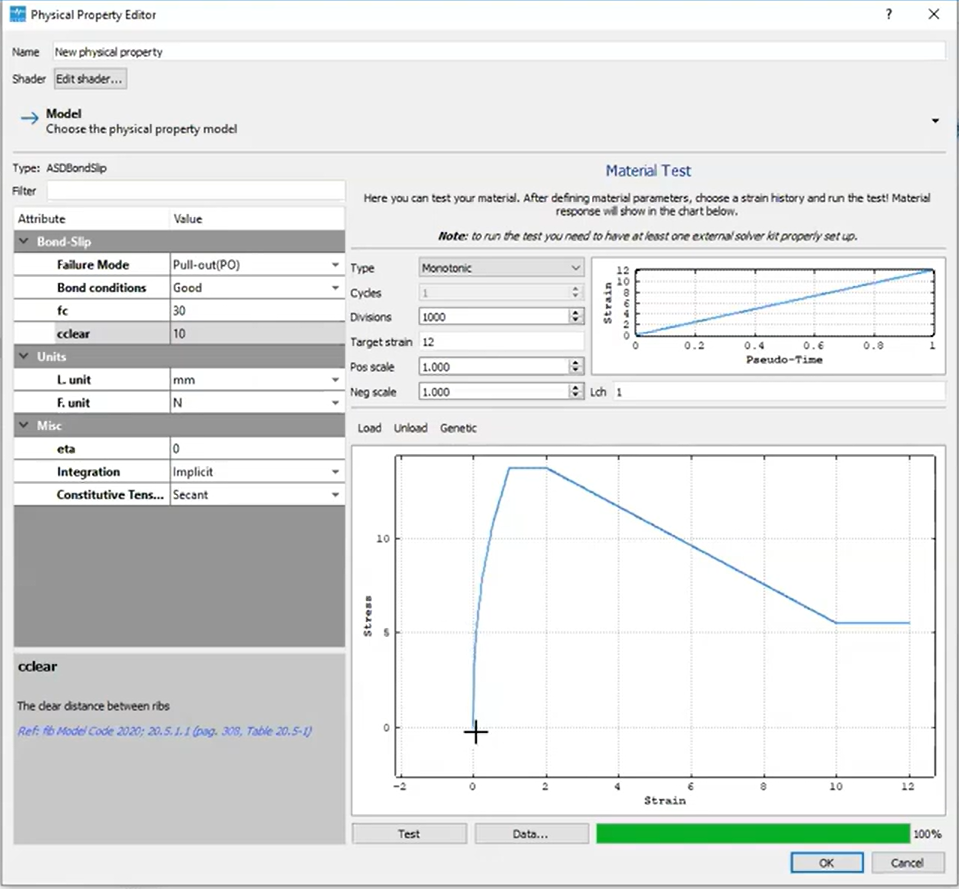
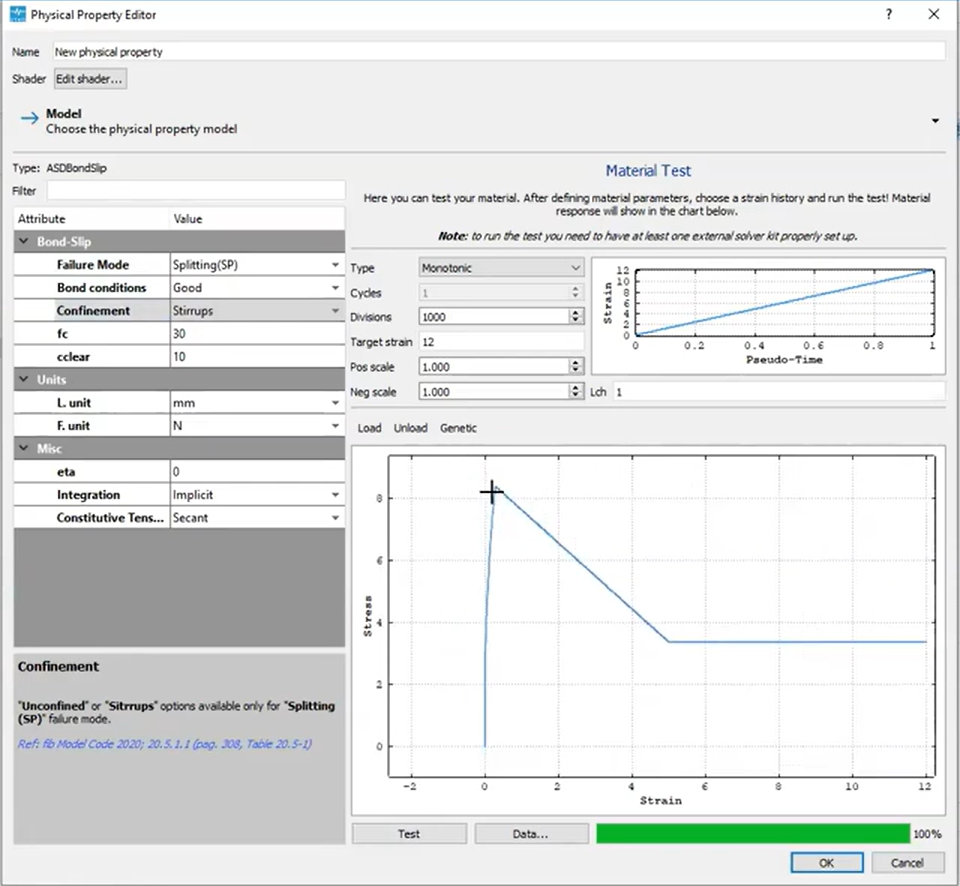
Bond-Slip Models from Code to Practice
The bond-slip model introduced in STKO 4.0.0 adheres to the Model Code 2020 for steel-concrete interactions. Engineers can input failure modes (e.g., pull-out or splitting), bond conditions, and rib spacing for precise modeling.
Pull-Out vs. Splitting Performance
- Pull-Out Mode: Higher ductility and a residual strength plateau.
- Splitting Mode: Earlier failure, weaker performance under poor bond conditions.
Why STKO 4 Matters
Structural engineering constantly pushes the boundaries of detail and accuracy. STKO 4.0.0 makes that pursuit easier by automating tedious tasks, improving visualization, and expanding material capabilities. Whether you’re building better masonry models or simplifying mass assignments, STKO saves time and reduces errors.
Take your projects further with features like cohesive zones, bond-slip modeling, and flexible constraint handling. STKO 4.0.0 makes complex problems manageable while ensuring results remain precise and reliable.
Click here to download: https://asdeasoft.net/file/STKO-4.0.0-Installer.exe or go to your user area on the webpage: https://asdea.eu/software/login/
If you have any questions about STKO, contact us.
Related Articles
The Importance of Seismic Design in Structural Engineering- Ensuring Safety in High-Risk Regions
Seismic design is essential for earthquake resilience. This blog explores key structural engineering principles, advanced techniques like capacity design, and the role of advanced simulation tools such as Asdea STKO for OpenSees and MonStr System in predicting and controlling damage evolution to ensure safer, more durable structures in high-risk regions.
Part 1 – Static: To Linear, or Not to Linear, That Is The Question
PrefaceStructural engineering has relied on linear analysis methods prescribed in design codes for decades to ensure safety and reliability. These methods are well-established, efficient, and familiar but have notable limitations. As designs become more complex,...
Structural Health Monitoring Innovations at WCEE 2024
Discover how our innovative MonStr system and AI-powered DigitalTwinning technology are revolutionizing structural health monitoring. Learn about our recent successes at WCEE 2024 and how we’re making infrastructure safer and more resilient.